Paper accepted in Environ Sci Technol
We just got word that a paper from Meret was accepted for publication in ES&T.
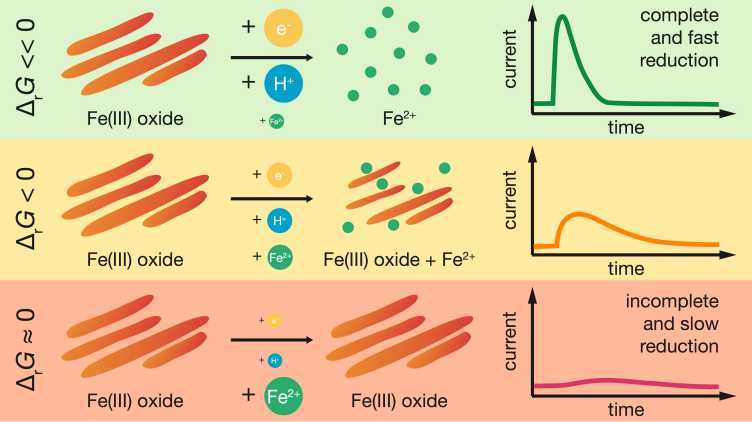
We just got word that a paper from Meret was accepted for publication in ES&T. Congratulations, Meret! In her work, Meret demonstrates that mediated electrochemical analysis can be used to systematically study rates and extents of iron (oxyhydr-)oxide reduction (shown for goethite, hematite and ferrihydrite) as a function of the thermodynamic boundary conditions for oxide reduction. The latter were systematically altered by varying the reduction potential applied to the electrochemical cell, the solution pH and the dissolved Fe2+ concentration in the cell. At intermediate negative free energies for oxide reduction, the natural logarithm of the reaction rate constant linearly correlated with the free energy, strongly suggesting that thermodynamics controlled the rate of reductive oxide dissolution. Meret further showed that the approach can be used to monitor decreases in the reducibility of oxides during transformation of amorphous to more crystalline phases, as shown for the Fe2+-catalyzed transformation of ferrihydrite to goethite.
Aeppli, M., A. Voegelin; C. Gorski, T. Hofstetter, and M. Sander. Mediated electrochemical reduction of iron (oxyhydr-)oxides under defined thermodynamic boundary conditions. Environ Sci Technol. 2017. asap, DOI: external page10.1021/acs.est.7b04483call_made
